The DUSD Stablecoin: Stable by Design

Stability is the bedrock that ensures the reliability and sustainability of financial systems. This is true both in traditional finance (TradFi) and the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector.
As DeFi continues to expand and integrate within TradFi, the need for stable assets that can withstand market volatility becomes increasingly crucial. In this context, the Davos Protocol offers one of the most relevant solutions within DeFi: the DUSD stablecoin.
Designed with robust mechanisms to maintain its stability, DUSD enables users to safely trade, park assets, and explore multiple staking strategies within prominent layer 1 and layer 2 ecosystems.
Read below to learn more about DUSD and the price stability mechanisms employed by the Davos Protocol to ensure its stability and sustainability.
Overview of Price Stability in DeFi
Stablecoins play a vital role in DeFi, providing a reliable medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account, facilitating smoother and more predictable transactions. Additionally, they facilitate the influx of capital into the crypto market.
As a brief recap, stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to a reserve of assets such as fiat currency and commodities, bridging the gap between traditional financial systems and the innovative world of DeFi. For a detailed overview of stablecoins and their function within the broader crypto industry, you can read our previous blog post here:
-> [Understanding Stablecoins in Defi: Mechanisms for Stability] (https://davos.xyz/blog/types-of-stablecoins/)
Now let us take a look at the mechanism that keep our stablecoin, DUSD, stable.
Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) and Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio
In DeFi, a Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) allows users to deposit assets as collateral to borrow against them. This mechanism enables users to leverage their holdings to generate liquidity without selling their assets.
Davos Protocol’s CDP Strategy:
- Over-Collateralization: The Davos Protocol enforces a 150% over-collateralization ratio. This means that for every $100 worth of DUSD issued, at least $150 worth of collateral is required, providing a significant safeguard against market volatility.
- Dynamic LTV Ratios: The protocol employs dynamic Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratios tailored to the risk profiles of different collateral types. For instance, Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) typically have an LTV ratio of 66%, allowing users to borrow up to $66 for every $100 of collateral. This approach ensures a secure and stable borrowing experience.
Liquidation Mechanisms
Safeguards Against Liquidation:
- Strategies and Ratios: Davos employs robust liquidation strategies, sound ratios, and penalties to protect against potential liquidation events.
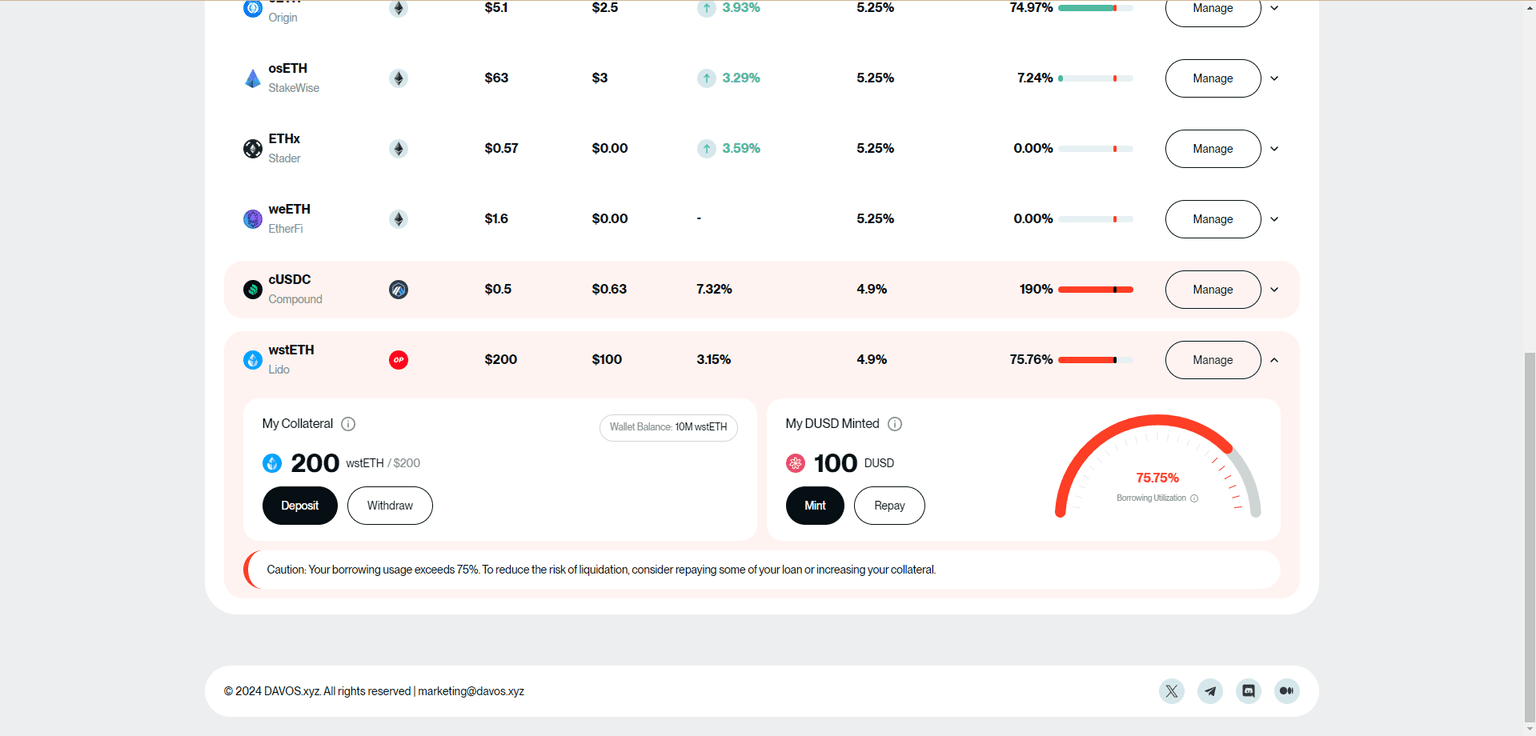 Borrowing Utilization Ratio on Dashboard ([Source]
(https://davos.xyz/app/dashboard/))
Borrowing Utilization Ratio on Dashboard ([Source]
(https://davos.xyz/app/dashboard/))
- Flash Mint Functionality: The Flash Mint feature allows instant minting of DUSD to settle outstanding balances and restore collateral. This seamless process ensures a smooth liquidation mechanism.
- Risk Management: Comprehensive risk management guidelines and monitoring systems bolster ecosystem stability, ensuring that the platform can handle market fluctuations effectively.
Monetary Policy Adjustment
Dynamic Borrowing Rates:
- Risk Adjustment: Higher borrowing rates for riskier collateral types help control supply and demand dynamics. This method ensures that the DUSD stablecoin remains stable and reliable within the broader financial landscape.
Arbitrage Mechanisms
Role of Arbitrage in Price Stability:
- Mechanism: Traders exploit price discrepancies between DUSD and other assets to profit, thereby realigning DUSD with its peg.
- Davos’s Approach: Instead of using a Peg Stability Module (PSM), Davos integrates reward-bearing assets from lending protocols. This strategy fosters profitable arbitrage opportunities and maintains DUSD’s market stability.
Reserve Pool
Purpose and Function:
- Financial Safety Net: The Reserve Pool is funded by a portion of the yield from accepted collateral types. It acts as a buffer against potential bad debt.
- Platform Stability: As loans increase, the Reserve Pool grows, reinforcing platform stability and user trust.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, the Davos Protocol employs several key price stability mechanisms to ensure that DUSD remains a stable and reliable asset within the DeFi ecosystem.
By enforcing healthy CDP and LTV ratios, dynamic monetary policy, arbitrage mechanisms, liquidation safeguards, and a Reserve Pool, the Davos Protocol provides a robust framework for maintaining DUSD’s constant peg to the US Dollar.
For more insights and updates on stablecoins and the DeFi space, follow our blog and stay informed about the latest trends and updates on X (Twitter).
Explore how Davos Protocol’s DUSD is shaping the future of stablecoins in DeFi.
